What is Bitcoin? About Bitcoin mining... (part 7)
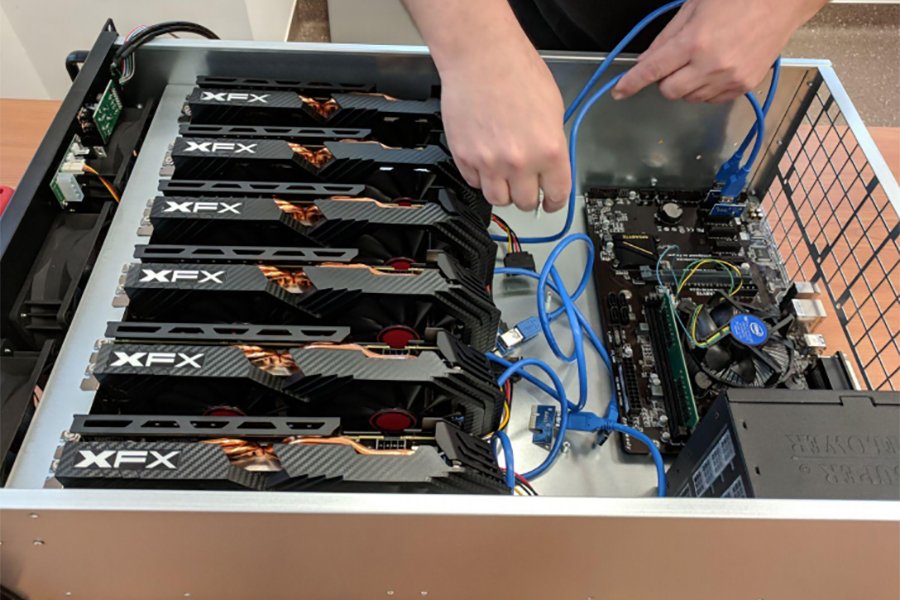
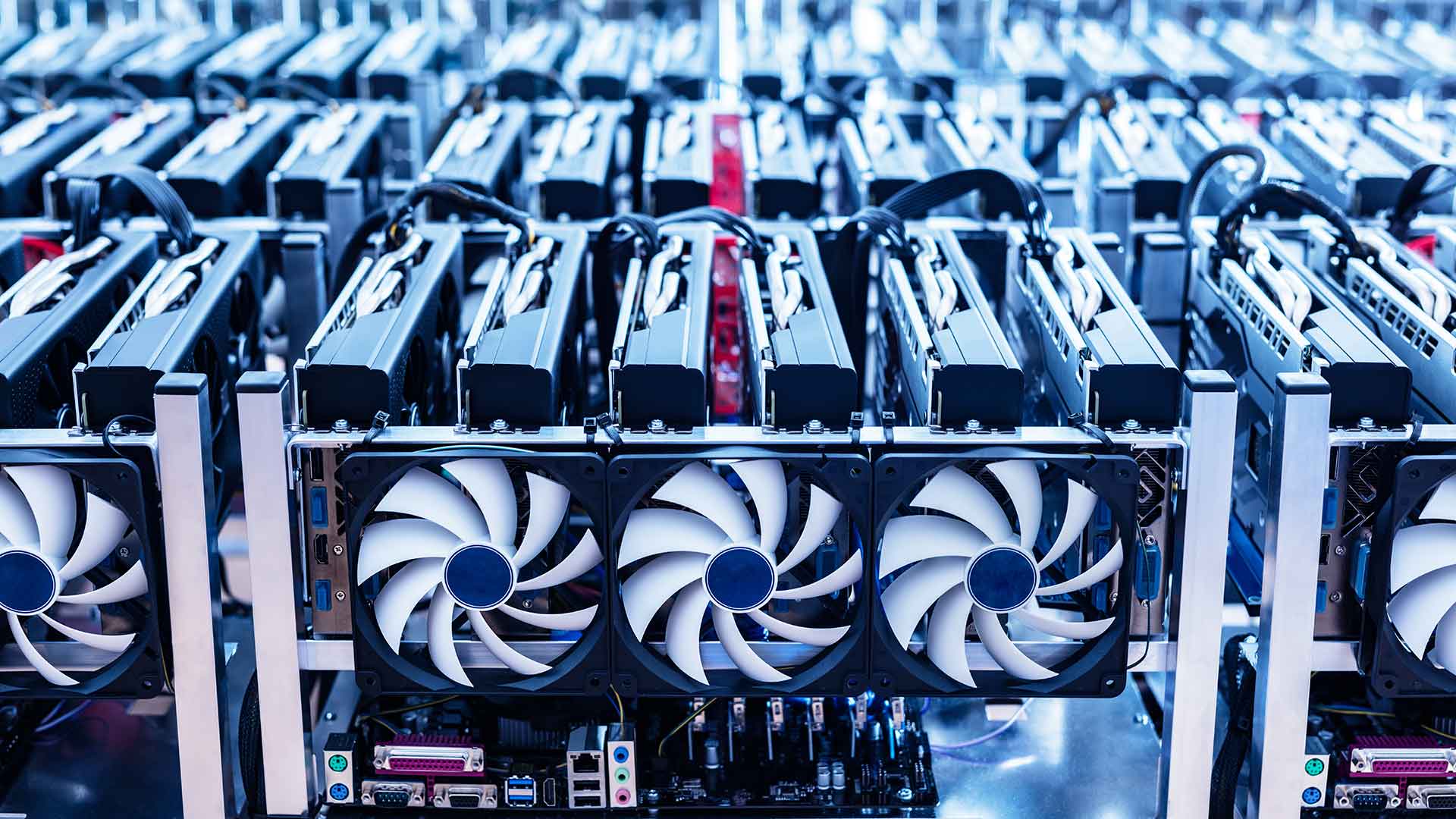
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new Bitcoins are created and transactions are verified on the Bitcoin network. Miners use specialized computer hardware to solve complex mathematical equations that validate transactions and add them to the blockchain, a public ledger of all Bitcoin transactions.
Miners are rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins for their efforts and also earn a transaction fee for each block they validate. The number of Bitcoins rewarded for each block decreases over time, and it is designed to reach zero by around the year 2140. This decrease in the rate of new Bitcoins being mined is built into the Bitcoin protocol to control inflation and mimic the scarcity of precious metals.
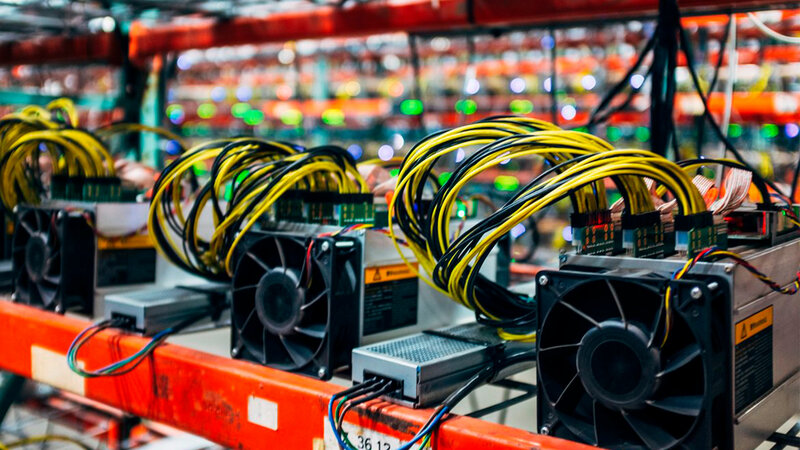
As the demand for Bitcoin increases, so does the difficulty of the mathematical equations that need to be solved by the miners. This means that more powerful and specialized equipment is needed to mine Bitcoin profitably. This has led to the centralization of mining, with large mining pools controlling a significant portion of the network's computational power.
It's also worth mentioning that the energy consumption associated with Bitcoin mining has been a topic of concern, as it requires a significant amount of computational power, and therefore electricity. Some estimates suggest that the energy consumption of the Bitcoin network is comparable to that of small countries. However, many experts believe that this problem can be addressed with advances in energy-efficient mining technology and the increased adoption of renewable energy sources.
Overall, Bitcoin mining is a crucial component of the Bitcoin network that helps to secure and validate transactions, while also creating new Bitcoins. It's a complex process that requires specialized equipment and a significant amount of computational power, but it is essential for the functioning and security of the Bitcoin network.

.jpg)
.jpg)











 English (US)
English (US)